Crawling vs Scraping: The Differences
Learn the difference between web crawler & scraper and how they benefit your business in our guide.


- What is data scraping?
- What is web scraping?
- What is crawling?
- Scraping vs crawling
- Data scraping for business
- Conclusion
Web scraping and web crawling are often mixed up, but they have different uses in business and technology. Here’s a brief overview before we get deeper into the differences between a web crawler and a web scraper:
Web scraping involves pulling data from websites, whereas web crawling is about finding URLs or links. While they might seem similar, there are distinct differences between the two. However, scraping and crawling are often used together in the data collection process, with one typically following the other.
What is data scraping?
Data scraping, sometimes confused with web scraping, involves collecting publicly accessible data from the internet or a computer and saving it to a local file on your computer. This data can also be transferred to another website. It’s a highly efficient method for gathering data from the web, and interestingly, it doesn’t always need an internet connection to work. Learn more about efficient scraping tools at Serply.
What is web scraping?
Web scraping involves collecting publicly available data from the internet and saving it to a file on your computer. The key distinction from data scraping is that web scraping requires an internet connection. Typically, this process is carried out using a Python scraper or a pre-built scraping tool like a Web Scraper API.
What is crawling?
Web crawling, also known as data crawling, is about gathering data, either from the web or documents and files. It’s typically done on a large scale using a crawler agent, visit Serply’s documentation.
As explained by Python developer Bernardas Alisauskas, a crawler is “a program that visits web pages to download their contents.” It searches online for:
- Specific data sought by the user.
- Additional sites to crawl.
For example, crawling a website might involve:
- Targeting a specific website, like http://example.com
- Identifying product pages.
- Collecting product information (such as prices, titles, and descriptions).
The information a crawler finds is then downloaded, a process that shifts into web or data scraping.
Throughout this discussion, we’ll use terms like data and web scraping or crawling interchangeably, mainly focusing on web scraping/crawling, despite the subtle differences between these concepts.
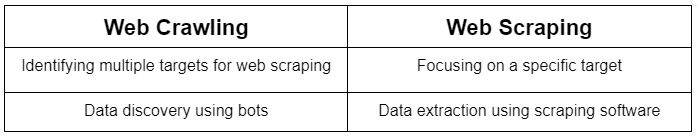
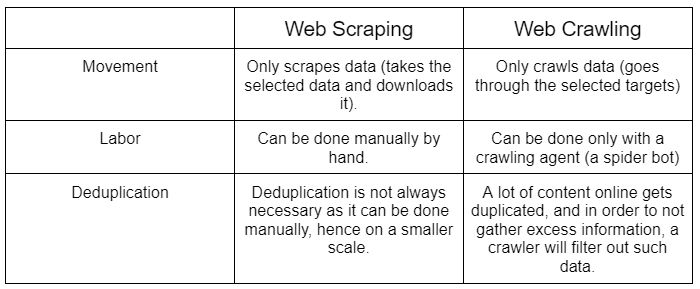
Scraping vs crawling
You may ask what is the difference between web scraping and crawling? Let’s answer that question.
To get the difference between scraping and crawling, remember that crawling is about looking through various places, like clicking on links. Scraping is when you take the data you’ve found and save it somewhere, like on your computer. When you scrape data, you’re specifically looking for certain things to collect, such as product details, prices, and descriptions. Discover more on this topic in our blog on scraping versus crawling.
It’s good to know how web crawling differs from web scraping, but they usually happen together. Crawling is when you collect all sorts of information from the internet, often from search engines or online stores. After crawling, you then scrape by picking out only the bits of data you really need, leaving the rest behind. Enhance your understanding of this process with our comprehensive guide.
Even though they are often used together, you can scrape data by itself without crawling, especially if you’re only looking for a little bit of information. On the other hand, crawling almost always comes with scraping to help sort through the data.
So, when we talk about scraping versus crawling, we’re looking at the big ways they differ and how each one is used to handle data online.
Data scraping for business
Data scraping has turned into a key strategy for growing businesses in recent years. A study by McKinsey Global Institute shows that companies focused on data are 23 times more likely to bring in new customers. They’re also six times more likely to keep those customers and 19 times more likely to be profitable. Using data helps businesses make smarter decisions and boost how customers feel about their service.
As more people use the internet, the number of companies relying on data keeps increasing. Forrester Research says these businesses grow by about 30% annually. It’s predicted that by 2021, they will earn $1.8 trillion more per year than companies that don’t use data as much.
Businesses that focus on data and insights do better than those that don’t. By keeping an eye on how customers interact with them and understanding customer behavior deeply, companies can make their customer service better. This improves how much customers value the service and makes them more loyal to the brand.
Data scraping plays a crucial role across various business sectors. As data becomes a key competitive asset, obtaining it is increasingly vital. Here are several areas where data scraping is significantly impacts business outcomes and drives deeper insights:
- Competitor Analysis and Pricing: Data scraping helps you understand competitors’ pricing information, monitoring changes, discounts, and online activities. It can also gather specific business details from directories like Yellow Pages.
- Marketing and Sales: Through data scraping, businesses can conduct comprehensive market research, collect additional leads, analyze consumer interests, and track public opinions by extracting customer reviews from various platforms. For instance, scraping real estate data keeps businesses competitive, while automotive data supports market predictions.
- Product Development: E-commerce site scraping is useful for finding product details or checking inventory status across numerous marketplaces and retail websites.
- PR, Brand, and Risk Management: Data scraping aids in detecting advertisement fraud, enhancing ad performances, verifying advertisers’ landing pages, and monitoring brand mentions for protective measures.
- Strategy Development: Building a strategy requires solid data. Scraping provides insights into industry trends, SEO monitoring, and the latest news, supporting strategic planning.
In each of these areas, data scraping empowers businesses to become more insight-driven, enhancing their competitive edge and operational efficiency.
Improving your business can also come from making your site more attractive to other companies that use web crawling. Being at the top of search engine results pages (SERPs) is crucial. You should consider how to make your website easier for search engines to find and index.
Search engines use algorithms with specific criteria to discover and catalog your site. It's the job of webmasters and SEO experts to optimize your website in a way that boosts its rankings and brings in more visitors, ultimately benefiting your business.
We’ve created an ebook on web scraping and its top strategies. Download it to discover more.
Conclusion
Now that we’ve clarified the terms data scraping, data crawling, and web scraping, let’s summarize. The key difference between web crawling and web scraping is that crawling involves navigating through data, while scraping is about downloading that data. The terms “web” and “data” also hint at where these activities occur: ‘web’ implies internet involvement, while ‘data’ might not necessarily involve the internet.
Data scraping is vital for businesses aiming to attract customers and grow their revenue. As the internet becomes a primary source for gathering business intelligence, the demand for scraping publicly available data will increase. This is essential for gaining insights and maintaining a competitive edge in the market.